Table of Contents
This outline focuses on providing a comprehensive comparison of propane and natural gas for various home applications, emphasizing the advantages of propane.
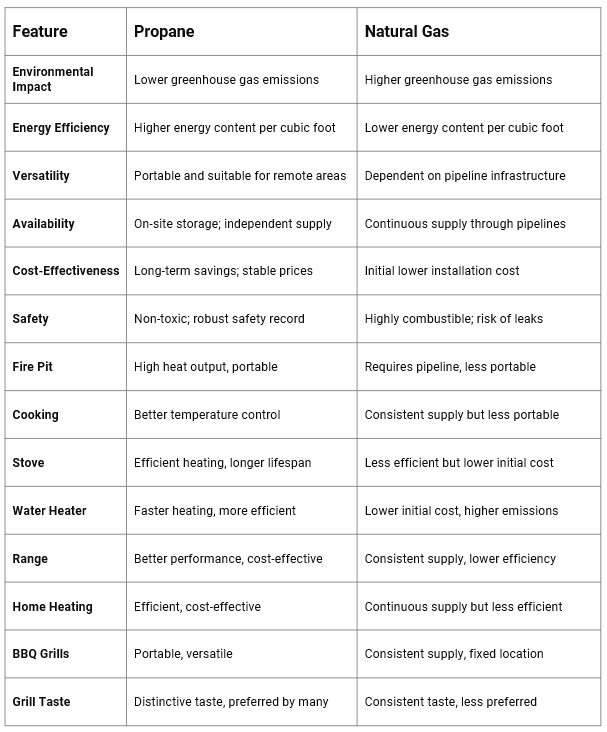
Environmental Impact
When comparing the environmental impact of propane and natural gas, propane emerges as the cleaner option. Propane combustion produces fewer greenhouse gases, including lower carbon dioxide levels, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. This results in a smaller carbon footprint and contributes to better air quality. In contrast, while cleaner than some fossil fuels, natural gas still emits higher levels of these pollutants.
Propane’s non-toxic nature also gives it an edge. If leaked, it does not harm soil or groundwater, whereas natural gas can pose significant environmental risks if it escapes into the ground. Propane’s cleaner burn and non-toxic properties make it more environmentally friendly than natural gas.
Pros and Cons of Propane
Pros
- Cleaner Burning: Produces fewer greenhouse gases, leading to lower carbon emissions.
- Higher Energy Content: More efficient, providing more heat per cubic foot.
- Versatility: Can be used for various applications, including heating, cooking, and powering appliances.
- Portability: Ideal for areas without pipeline infrastructure; stored in on-site tanks.
- Environmental Safety: Non-toxic, does not contaminate soil or groundwater.
- Stable Pricing: Often more stable prices, with opportunities for bulk purchasing.
Cons
- Initial Installation Cost: Higher initial cost for setting up propane systems and tanks.
- Storage Requirements: Requires space for on-site tanks.
Pros and Cons of Natural Gas
Pros
- Continuous Supply: Delivered through pipelines, providing a consistent supply without needing on-site storage.
- Lower Initial Cost: Generally lower installation costs compared to propane.
- Widely Available: Extensive pipeline infrastructure in many urban and suburban areas.
Cons
- Higher Emissions: Produces more greenhouse gases, contributing to a larger carbon footprint.
- Lower Energy Content: Less efficient, requiring more fuel to produce the same heat.
- Environmental Risk: Potential for soil and groundwater contamination in case of leaks.
- Dependent on Infrastructure: Limited to areas with existing pipeline networks, less suitable for remote locations.
Energy Efficiency
Regarding energy efficiency, propane has a clear advantage over natural gas. Propane contains approximately 2,516 BTUs (British Thermal Units) per cubic foot, while natural gas contains about 1,030 BTUs per cubic foot. This means propane delivers more than twice the energy of natural gas per unit of volume, making it a more efficient fuel.
In practical terms, this higher energy content translates to better performance in heating systems and appliances. Propane-powered appliances typically heat up faster and maintain consistent temperatures, leading to lower fuel consumption and reduced energy costs. For instance, a propane water heater can heat water quicker and more efficiently than a natural gas model, providing both comfort and savings.
Furthermore, propane’s efficiency is evident in its use in home heating. Propane furnaces often achieve efficiency ratings of 90% or higher, compared to the 78-95% efficiency range for natural gas furnaces. This higher efficiency means less fuel is needed to achieve the same level of heating, resulting in lower utility bills and a reduced environmental impact.
Overall, propane’s higher energy content and greater efficiency make it a superior choice for homeowners looking to maximize their energy use and minimize costs.

Versatility and Availability
Propane’s versatility and availability make it an attractive option for many homeowners. Unlike natural gas, which relies on a fixed pipeline infrastructure, propane can be stored in on-site tanks, making it accessible in urban and remote areas. This flexibility ensures a reliable energy source regardless of location, especially in regions without natural gas pipelines.
Propane can be used for various applications, including home heating, cooking, water heating, and powering appliances like dryers and generators. Its portability also makes it ideal for outdoor use, such as fueling BBQ grills and fire pits. This adaptability is a significant advantage over natural gas, as it is confined to areas with existing pipeline networks and is less suitable for portable applications.
Another benefit of propane is its independence from utility companies. Homeowners can manage their fuel supply directly, ensuring enough fuel during peak demand periods or emergencies. This on-site storage capability provides a buffer against supply interruptions, which can be a concern with natural gas, especially during natural disasters or infrastructure failures.
Moreover, propane suppliers often offer flexible delivery and payment plans, allowing homeowners to plan fuel purchases according to their needs and budgets. In contrast, natural gas consumers are tied to their local utility companies’ pricing and supply conditions, which can vary and sometimes be less predictable.
Propane’s versatility, widespread availability, and independence from pipeline infrastructure make it a more practical and reliable energy choice for various residential applications.
Cost-Effectiveness
Propane offers significant long-term cost savings compared to natural gas despite the higher initial installation costs associated with setting up propane systems and storage tanks. These savings stem from several key factors: fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and price stability.
Fuel Efficiency: Propane’s higher energy content means less fuel is required to achieve the same heating output as natural gas. This efficiency translates to lower overall fuel consumption, which can significantly save energy bills over time. For example, propane water heaters and furnaces generally consume less fuel to produce the same amount of heat as their natural gas counterparts, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Maintenance and Appliance Lifespan: Propane appliances typically have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance than natural gas appliances. The cleaner burn of propane results in less soot and residue buildup, which reduces wear and tear on appliances and extends their operational life. This longevity minimizes the need for frequent replacements and repairs, further lowering maintenance costs.
Price Stability: Propane prices tend to be more stable than natural gas prices, which fluctuate due to market conditions and geopolitical factors. Propane users can buy fuel in bulk during periods of lower prices, allowing them to manage their energy expenses more effectively. Additionally, many propane suppliers offer fixed-price contracts and budget plans, providing homeowners with predictable and manageable energy costs.
Flexibility in Purchasing: Homeowners using propane can choose from various suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and service options. This competition can lead to better rates and customer service compared to the often monopolistic supply of natural gas, where consumers are limited to the rates and terms set by their local utility provider.
In summary, while the initial setup for propane may be higher, the long-term cost-effectiveness due to its fuel efficiency, lower maintenance needs, and price stability make propane a financially savvy choice for homeowners.
Safety Considerations
When evaluating safety, propane has several advantages over natural gas. Both fuels are highly combustible and require careful handling, but propane’s properties and safety measures make it a safer choice for residential use.
Non-Toxic Nature: Propane is non-toxic and does not pose a risk to soil or groundwater in the event of a leak. This contrasts natural gas, which can contaminate the environment if it escapes from pipelines. Propane leaks dissipate quickly into the air, minimizing the risk of long-term environmental damage.
Storage and Leak Detection: Propane is stored in pressurized tanks with multiple safety features, including shut-off valves and pressure relief devices. These tanks are designed to withstand extreme conditions, reducing the risk of leaks and explosions. Additionally, propane is naturally odorless, but an odorant is added to detect leaks easily. While natural gas also has an odorant added for leak detection, propane storage systems are generally more robust and secure.
Lower Ignition Risk: Propane has a narrower flammability range compared to natural gas, making it less likely to ignite in the event of a leak. The lower ignition risk of propane means that accidental fires and explosions are less likely, enhancing overall safety for homeowners.
Regulatory Oversight and Industry Standards: The propane industry is highly regulated, with stringent safety standards and practices to ensure safe handling, storage, and fuel use. Propane suppliers and technicians undergo rigorous training and certification processes, ensuring that installations and maintenance are conducted safely and effectively. While natural gas is also regulated, propane’s portability and storage requirements necessitate additional safety measures that often result in a higher safety compliance standard.
Emergency Preparedness: Propane’s ability to be stored on-site provides an added layer of safety during emergencies, such as natural disasters. Unlike natural gas, which relies on a continuous pipeline supply that can be disrupted, propane tanks provide a reliable and accessible energy source when other utilities may be compromised.
In summary, propane’s non-toxic nature, robust storage systems, lower ignition risk, and stringent safety regulations make it a safer option for residential use than natural gas.
Specific Applications and Comparisons
Propane vs. Natural Gas Fire Pit
Efficiency and Heat Output: Propane fire pits typically offer higher heat output and efficiency than natural gas ones. Propane’s higher energy content ensures that the fire burns hotter and more consistently, providing a more effective heating solution for outdoor spaces.
Portability: Propane fire pits are portable and can be easily moved and set up in various locations, unlike natural gas fire pits, which are fixed due to their reliance on pipeline connections.
Installation Costs: Propane fire pits generally have lower installation costs since they do not require a connection to a natural gas pipeline.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Cooking
Temperature Control: Propane provides better temperature control and heats up faster, making it ideal for precision cooking. Many professional chefs prefer propane for its responsive and consistent heat.
Fuel Availability: Propane is readily available in portable tanks, making it a convenient option for outdoor cooking and in areas without natural gas infrastructure.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Stove
Heating Efficiency: Due to propane’s higher energy content, propane stoves typically heat up faster and provide more consistent cooking temperatures.
Fuel Costs: While natural gas stoves may have lower initial fuel costs, propane stoves offer better long-term efficiency and savings on fuel consumption.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Emissions
Greenhouse Gases: Propane emits fewer greenhouse gases than natural gas, making it a cleaner option for the environment.
Air Quality: Propane’s lower emissions of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide contribute to better air quality and reduced environmental impact.

Propane vs. Natural Gas Water Heater
Heating Speed: Propane heaters heat water faster than natural gas models, providing a quick and efficient hot water supply.
Energy Efficiency: Propane water heaters are generally more energy-efficient, consuming less fuel to achieve the desired water temperature.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Range
Cooking Performance: Propane ranges offer superior cooking performance with precise temperature control and faster heating times.
Fuel Efficiency: Propane’s higher energy content makes it more fuel-efficient, leading to lower overall energy costs.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Home Heating
Heating Efficiency: Propane furnaces often have higher efficiency ratings, translating to better heating performance and lower fuel consumption.
Cost-Effectiveness: The long-term cost savings due to propane’s efficiency and stable pricing make it a more economical choice for home heating.
Propane vs. Natural Gas BBQ Grills
Taste and Cooking Performance: Many users prefer the taste of food cooked on propane grills, which can achieve higher temperatures and provide a distinct grilling experience.
Portability: Propane BBQ grills are portable and can be used outdoors, while natural gas grills are fixed and limited to areas with pipeline access.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Grill Taste
Flavor Difference: Propane grills often produce a more intense and distinct flavor due to the higher heat output and the way propane burns.
Cooking Preferences: Propane grills are usually preferred for those who prioritize flavor and grilling versatility.
In summary, propane consistently offers superior performance, efficiency, and versatility across various applications, making it a better choice for many homeowners than natural gas.

BBQ Grills: Propane vs. Natural Gas
Several factors come into play when choosing between a natural gas or propane BBQ grill, including taste, convenience, and performance. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you make the right choice for your grilling needs.
Taste and Cooking on Propane Grills
Higher Heat Output: Propane grills can reach higher temperatures faster, which is ideal for searing meats and achieving that perfect char.
Distinct Flavor: Many grill enthusiasts prefer the taste of food cooked on propane grills, as the higher heat and faster cooking times can enhance the smoky flavors.
Versatility: Propane grills are known for their excellent heat distribution and consistent performance, making them suitable for various cooking styles, from slow roasting to high-heat grilling.
Taste and Cooking on Natural Gas Grills
Consistent Supply: Natural gas grills provide a continuous fuel supply from a fixed pipeline, eliminating the need to refill tanks.
Lower Initial Fuel Cost: Natural gas tends to be cheaper per unit than propane, which can result in lower operational costs over time.
Stable Cooking: While they may not reach the high temperatures of propane grills as quickly, natural gas grills still offer stable and consistent cooking performance.
Portability and Convenience of Propane Grills
Portable: Propane grills are highly portable and can be easily moved to different locations, making them ideal for camping, tailgating, and backyard parties.
Easy Setup: Setting up a propane grill is straightforward. It only requires connecting a propane tank without needing a gas line installation.
Readily Available: Propane tanks are widely available and can be refilled or exchanged at numerous locations, adding to their convenience.
Portability and Convenience of Natural Gas Grills
Fixed Location: Natural gas grills are connected to a gas line, making them a permanent fixture in your outdoor kitchen. This lack of portability can be a drawback for those who want flexibility.
Initial Installation: Installing a natural gas grill requires a professional to connect it to your home’s gas line, which can involve additional costs and planning.
No Refueling: One of the main advantages is that natural gas grills don’t need refueling. You have an endless gas supply if your home’s gas line is active.
Cost and Maintenance of Propane Grills
Fuel Costs: While propane is typically more expensive per BTU than natural gas, the efficiency and higher heat output can balance this cost over time.
Maintenance: Propane grills require regular maintenance, including checking the tank and connectors for leaks, but this is generally straightforward.
Cost and Maintenance of Natural Gas Grills
Lower Fuel Cost: Natural gas is often less expensive than propane, resulting in lower long-term fuel costs.
Installation Costs: The initial cost of installing a natural gas line can be high, but it’s a one-time expense. Maintenance involves ensuring the gas line and connections are secure.
Propane vs. Natural Gas Grill Taste
Many grilling enthusiasts strongly prefer the taste of food cooked on natural gas versus propane grills. The type of fuel used can influence the flavor and overall cooking experience, with each offering distinct advantages.
Propane Grill Taste
Higher Heat Output: Propane grills can reach higher temperatures faster than natural gas grills. This higher heat is ideal for searing meats, creating a caramelized crust that enhances the flavor of steaks, burgers, and other grilled items.
Flavor Enhancement: The intense, direct heat from propane grills can create a smokier, more pronounced flavor in foods. This is particularly noticeable when grilling items that benefit from a quick sear, like vegetables and seafood.
Versatile Cooking Styles: Propane’s ability to provide consistent high heat makes it suitable for various cooking styles, from slow cooking and smoking to fast, high-temperature grilling. This versatility can result in more complex and layered flavors in your dishes.
Natural Gas Grill Taste
Consistent Cooking Temperature: Natural gas grills offer a steady, consistent temperature ideal for evenly-cooking foods. This consistency can benefit longer cooking processes, such as roasting or baking on the grill, where maintaining a uniform temperature is crucial.
Subtle Flavor: While natural gas grills may not impart as strong a smoky flavor as propane grills, they still produce excellent results, especially for foods that require a gentler cooking process. The more moderate heat can help preserve the natural flavors of delicate items like fish and poultry.
Convenience and Control: The continuous supply of natural gas means you can cook for extended periods without worrying about running out of fuel. This convenience can translate to a more relaxed grilling experience, allowing you to focus on perfecting the taste and texture of your food.
Taste Preferences and Cooking Goals
Conclusion
Choosing the right fuel for your home involves weighing the benefits and drawbacks of propane and natural gas across various applications. Throughout this article, the advantages of propane are highlighted, showcasing its superior energy efficiency, environmental impact, versatility, cost-effectiveness, safety, and performance in specific home and outdoor applications.
Propane stands out for its:
- Higher Energy Content: Providing more heat per cubic foot, leading to better efficiency and lower fuel consumption.
- Environmental Benefits: Producing fewer greenhouse gases and being non-toxic to soil and groundwater.
- Versatility and Portability: It is suitable for areas without natural gas pipelines and ideal for portable applications like BBQ grills and fire pits.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Offering long-term savings despite higher initial setup costs, with stable pricing and bulk purchasing options.
- Safety: Featuring robust storage systems, lower ignition risk, and stringent regulatory oversight.
- Performance: Excelling in applications such as cooking, water heating, home heating, and grilling, with faster heating times and better flavor enhancement.
While natural gas has its merits, such as a continuous supply and lower initial costs, propane’s advantages make it a compelling choice for homeowners seeking efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability.
In summary, propane offers a versatile, efficient, and environmentally friendly alternative to natural gas, making it a preferred option for many homeowners. By choosing propane, you can enjoy the benefits of a cleaner, more efficient fuel that meets a wide range of residential needs while contributing to a healthier planet. Contact one of our professionals at HOP Energy today to learn more and get started with propane!




