What is a Propane Generator?
A propane generator is a backup power system that generates electricity using propane gas. Unlike gasoline or diesel generators, which rely on liquid fuels that can degrade over time, propane generators utilize a stable and usable gas even after extended storage periods.
Propane generators convert propane gas into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy. This efficient and reliable process makes propane generators a popular choice for residential and commercial use, particularly during power outages.
Table of Contents
Why Propane is a Superior Choice for Home Backup Power
Propane’s cleaner-burning properties result in fewer emissions, making it an environmentally friendly option compared to gasoline or diesel. Additionally, propane’s consistent availability and lower operational costs make it a cost-effective choice in the long run. Propane generators require less maintenance, leading to lower upkeep costs and longer service life.
Investing in a propane generator is a step towards ensuring household resilience and contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable energy solution. Homeowners are encouraged to explore propane generator options and consult with professionals at HOP Energy to select the right system.

Comparison with Gas and Diesel Generators
Propane generators offer several advantages over their gasoline and diesel counterparts. Firstly, propane is a cleaner-burning fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and a lower environmental impact. This makes propane generators an environmentally friendly option, especially in areas with strict air quality regulations.
Secondly, propane is readily available and can be stored indefinitely without the risk of spoilage, unlike gasoline, which can deteriorate over time. This extended shelf life ensures that propane is always ready for use when needed, providing peace of mind during emergencies.
Lastly, propane generators typically require less maintenance than gasoline or diesel generators. The clean-burning nature of propane results in less carbon buildup in the engine, reducing wear and tear and extending the generator’s lifespan. This reliability and reduced maintenance need make propane generators a practical and cost-effective solution for long-term use.
Benefits of Propane Generators
Reliability and Efficiency
Propane generators are known for their reliability and efficiency. They consistently perform during power outages, ensuring that your home or business remains powered without interruption. One key advantage is that propane generators are less prone to fuel-related issues that can affect gasoline or diesel generators, such as clogged fuel lines or fuel degradation. This reliability is crucial during emergencies when continuous power is needed the most.
Environmental Impact
One of the standout benefits of propane generators is their reduced environmental impact. Propane is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to gasoline and diesel. When burned, it produces fewer pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and particulate matter. This means using a propane generator helps lower your carbon footprint and improves air quality. Propane generators offer a more eco-friendly power solution for those concerned about environmental sustainability.
Fuel Storage and Availability
Propane has significant advantages in terms of storage and availability. Unlike gasoline, which can degrade over time and require additives to stabilize, propane can be stored indefinitely without losing effectiveness. This makes it an ideal fuel for emergency preparedness. Propane is also widely available, and during natural disasters, it is often more accessible than gasoline or diesel, which can run out quickly due to high demand. The ability to safely store large quantities of propane for extended periods ensures that you always have a reliable fuel source.
These benefits make propane generators a compelling choice for those looking for a dependable, environmentally friendly, readily available power solution during outages.
Practical Considerations for Using Propane Generators
Can You Power a House with a Propane Generator?
Yes, you can power a house with a propane generator. Propane generators are designed to provide sufficient power to run essential household appliances, lighting, heating systems, and even entire homes, depending on the generator’s capacity. When selecting a propane generator for your home, it’s important to consider the power requirements of your essential appliances and systems to ensure the generator can handle the load.
How Long Will a Propane Generator Power a House?
The duration a propane generator can power a house depends on several factors, including the generator’s size, the load being powered, and the amount of propane available. For instance, a 7kW propane generator running at full load might consume around 1.42 gallons of propane per hour. With a 500-gallon propane tank, this generator could run for approximately 350 hours, or about two weeks, if operating continuously at full load. Actual runtime will vary based on the generator model and the household power demand.

How Far Does a Propane Generator Need to Be Away from the House?
Safety regulations typically require that propane generators be placed a certain distance from the house to ensure proper ventilation and reduce the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Generally, a propane generator should be placed at least 5 to 10 feet away from the house. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and local building codes when installing a propane generator is crucial to ensure safe and efficient operation.
What Size Propane Generator Do I Need for My House?
Determining the appropriate size of a propane generator for your house involves calculating the total wattage required to power your essential appliances and systems. To do this, list all the appliances and systems you need to run during a power outage and note their wattage. Add up the wattage to find the total power requirement. As a rule of thumb, choosing a generator with a slightly higher capacity than your total wattage needs is advisable to account for any additional or unforeseen power demands.
Considering these practical aspects, homeowners can make informed decisions about selecting and using propane generators to ensure they provide reliable power during outages.
Cost and Efficiency Analysis
What Size Propane Generator Do I Need for My House?
Propane is generally cheaper to run than gasoline due to its more stable pricing and higher energy efficiency. While propane generators may have a higher initial cost, the lower operational costs and longer shelf life of propane often result in overall savings. Propane prices are less volatile than gasoline prices, providing more predictable fuel costs.
How Much Propane Does a Generac Use in 24 Hours?
The fuel consumption of a Generac propane generator varies by model and load. For example, a 22kW Generac generator running at full load consumes about 3.9 gallons of propane per hour. Over 24 hours, this amounts to approximately 93.6 gallons. Actual consumption will be lower at partial loads, which is typical in most household scenarios.
How Long Will a 100 lb Propane Tank Last on a Generator?
A 100-lb propane tank holds approximately 23.6 gallons of propane. If a generator consumes 1.42 gallons per hour (7kW generator at full load), a 100-lb tank would last around 16.6 hours. Runtime can be extended by reducing the load or using the generator intermittently.
How Long Will a 500-Gallon Propane Tank Last for a Whole House Generator?
A 500-gallon propane tank holds about 400 gallons of usable propane. If a whole house generator consumes 2 gallons per hour, the tank would provide around 200 hours of power. This equates to over eight days of continuous use at full load, offering substantial coverage during extended outages.
Users can better manage fuel consumption and costs when using propane generators by understanding the cost and efficiency aspects.
Safety and Maintenance
Is it Safe to Use a Propane Generator Indoors?
No, it is not safe to use a propane generator indoors. Propane generators produce carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas that can be deadly in enclosed spaces. To prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, continuously operate propane generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas away from doors, windows, and vents.
Can You Run a Propane Generator 24 Hours a Day?
You can run a propane generator 24 hours a day, but it requires regular maintenance and monitoring. The continuous operation generates heat and wear on the engine, so following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, including oil changes and inspections, is essential. Ensure adequate fuel supply and allow the generator to cool down periodically if needed.
What Size Propane Generator Do I Need for My House?
To determine the right size propane generator, calculate the total wattage of all essential appliances and systems you need to power. Depending on the load, a typical home might require a generator with a capacity ranging from 7kW to 22kW. Consult with a professional to assess your power needs accurately and select an appropriately sized generator.
Propane generators can provide reliable power without compromising safety by adhering to safety guidelines and conducting regular maintenance.
Potential Downsides of Propane Generators
While propane generators offer many benefits, they also have some drawbacks. The initial cost of purchasing a propane generator can be higher compared to gasoline or diesel generators. Additionally, installation might require professional assistance, particularly if integrated with an existing propane system.
Initial Costs and Installation
The upfront expense of a propane generator and its installation can be significant. Professional installation is often necessary to ensure safe and efficient operation, adding to the initial investment. This cost can be a barrier for some homeowners.

Fuel Availability
Propane might not be as readily available in certain regions as gasoline or diesel. If local propane suppliers are unable to meet demand during extended outages, this could pose a challenge. To mitigate this risk, it’s crucial to have a sufficient supply of propane stored safely.
Storage Requirements
Propane tanks require proper storage to ensure safety. Large tanks, such as 500-gallon tanks, need adequate space and must adhere to safety regulations, including placement away from the house and other structures. These storage requirements can be cumbersome for some homeowners.
Performance in Cold Weather
Propane can be less efficient in extremely cold weather. The gas tends to liquefy at low temperatures, affecting the generator’s performance. Maintaining reliable operation is necessary to ensure that propane tanks and lines are adequately insulated and protected from the cold.
Understanding these potential downsides helps homeowners make informed decisions when considering propane generators for their power needs.
Practical Examples and User Experiences
Real-World Usage Scenarios
Homeowners who have invested in propane generators often share positive experiences, especially during prolonged power outages caused by severe weather events. For instance, in regions prone to hurricanes, many users report that propane generators provide:
- A reliable and long-lasting power supply
- It allows them to maintain essential household functions such as refrigeration
- Heating
- Medical equipment operation
Comparison Chart of Propane, Gasoline, and Diesel Generators
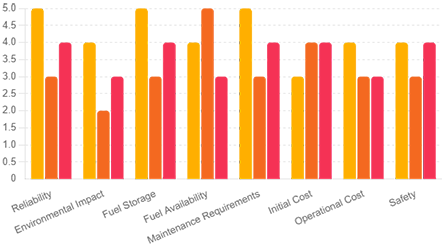
A comparison chart of propane, gasoline, and diesel generators across various criteria is here. The chart visually represents how each type of generator rates in terms of reliability, environmental impact, fuel storage, fuel availability, maintenance requirements, initial cost, operational cost, and safety.
- Propane Generators generally score high on reliability, environmental impact, fuel storage, and maintenance requirements but have a higher initial cost.
- Gasoline Generators are more readily available and have a lower initial cost but score lower on environmental impact and maintenance.
- Diesel Generators offer good reliability and reasonable fuel storage, with moderate initial and operational costs, but they have a moderate environmental impact and availability.
This comparison helps illustrate the strengths and weaknesses of each generator type, aiding in making an informed decision based on specific needs and priorities.
How to Choose Generator Capacity
Selecting the right generator capacity for your needs involves assessing your power requirements and understanding the generator’s capabilities. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the appropriate generator capacity:
Determine Your Power Needs
- List Essential Appliances: Identify all the essential appliances and systems you need to power during an outage (e.g., refrigerator, lights, heating/cooling systems, medical equipment, etc.).
- Check Power Ratings: Find the wattage requirement for each appliance. This information is usually found on the appliance label or user manual. If it needs to be listed, you can check the manufacturer’s website or use an online wattage chart.
- Calculate Total Wattage: Add up the wattages of all the essential appliances. Be sure to account for starting wattage, which is higher than running wattage for appliances with motors (like refrigerators and air conditioners).
Consider Surge and Running Wattage
- I am running Wattage: The continuous power required to keep an appliance running.
- Surge Wattage is the extra power needed to start an appliance. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 watts to run but 2200 watts to start.
- Total Wattage: Ensure your generator can handle your appliances’ total running and surge wattages simultaneously.
Choose a Generator with Appropriate Capacity
- Calculate Buffer: Add a buffer (usually 20-25%) to your total wattage to ensure the generator can handle unexpected power demands.
- Match Capacity: Select a generator with a wattage capacity that meets or exceeds your calculated total wattage, including the buffer. For example, if your total wattage requirement is 5000 watts, you should choose a generator with at least 6000 watts capacity.
Types of Generators
- Portable Generators are suitable for smaller power needs and can be easily moved. Typical capacities range from 2000 to 7000 watts.
- Standby Generators: Permanently installed and connected to your home’s electrical system. It is ideal for whole-house power needs, with capacities ranging from 7,000 to 22,000 watts.
Professional Assessment
- Consult an Electrician: For an accurate assessment, especially if you have complex power needs, consult a licensed electrician. They can calculate your exact power requirements and recommend an appropriate generator size.
Example Calculation
List appliances and their wattage:
- Refrigerator: 700 watts (running), 2200 watts (starting)
- Lights: 300 watts
- Heater: 1500 watts
- Television: 200 watts
- Total running wattage: 700 + 300 + 1500 + 200 = 2700 watts
Account for surge wattage:
- Highest starting wattage: 2200 watts (refrigerator)
- Total surge wattage: 2700 + 2200 = 4900 watts
Add buffer:
- 4900 watts + 25% = 6125 watts
Select a generator:
- Choose a generator with at least 6500 watts capacity.
Conclusion
Propane generators offer many benefits, making them an excellent choice for homeowners seeking reliable backup power during outages. Their key advantages include reliability, efficiency, environmental friendliness, and ease of fuel storage. Propane’s long shelf life and stability ensure that generators are ready for use whenever needed, providing peace of mind during emergencies. Contact HOP Energy today to learn more about our propane generators.




