Choosing the correct propane tank size is crucial for efficient energy use in your home.
Propane is a versatile and widely used fuel source that powers appliances such as stoves, water heaters, and home heating systems. The right tank size ensures uninterrupted service and optimizes operational costs and safety.
This guide our HVAC technicians created provides clear information on various propane tank sizes and how to select the best one based on your household needs.
Table of Contents
Understanding Propane Usage in Homes
Propane is a preferred energy source for various residential applications due to its efficiency and reliability. Key uses in homes include:
- Heating: Propane furnaces provide high-heat output and are more efficient than some electric models.
- Cooking: Gas stoves and ovens with propane offer precise temperature control and consistent heat.
- Water Heating: Propane water heaters heat water faster and are available in tank and tankless models.
- Clothes Drying: Propane dryers dry clothes more quickly and with less static cling than electric dryers.
- Pool Heating: Propane is commonly used for efficient swimming pool heating, allowing for longer swimming seasons.
- Outdoor Kitchens: Propane powers grills and cooktops in outdoor kitchens, providing convenient and reliable cooking options.
Propane consumption varies significantly based on the type and number of appliances used and individual usage patterns. A household that uses propane for both heating and cooking will have much higher demand in colder months than a home using propane strictly for cooking.
Types of Propane Tanks and Cylinders
Propane is stored in tanks and cylinders, each serving different applications and installation scenarios:
- Propane Tanks: Large units typically used for residential heating, cooking, and other energy needs. They may be installed above ground or underground.
- Above-ground tanks are easier to install and maintain, but they are more vulnerable to temperature changes and are visible in your yard.
- Underground tanks are aesthetically preferred as they are hidden from view; these tanks are protected from the elements but are more expensive to install.
- Propane Cylinders: Smaller and portable; ideal for barbecue grills, portable heaters, and small appliances. Size options range from tiny 1-pound cylinders for camping to larger 100-pound cylinders for temporary or supplementary residential use.
Choosing between a tank or cylinder depends on your usage frequency, quantity needed, and whether the installation is permanent or temporary.
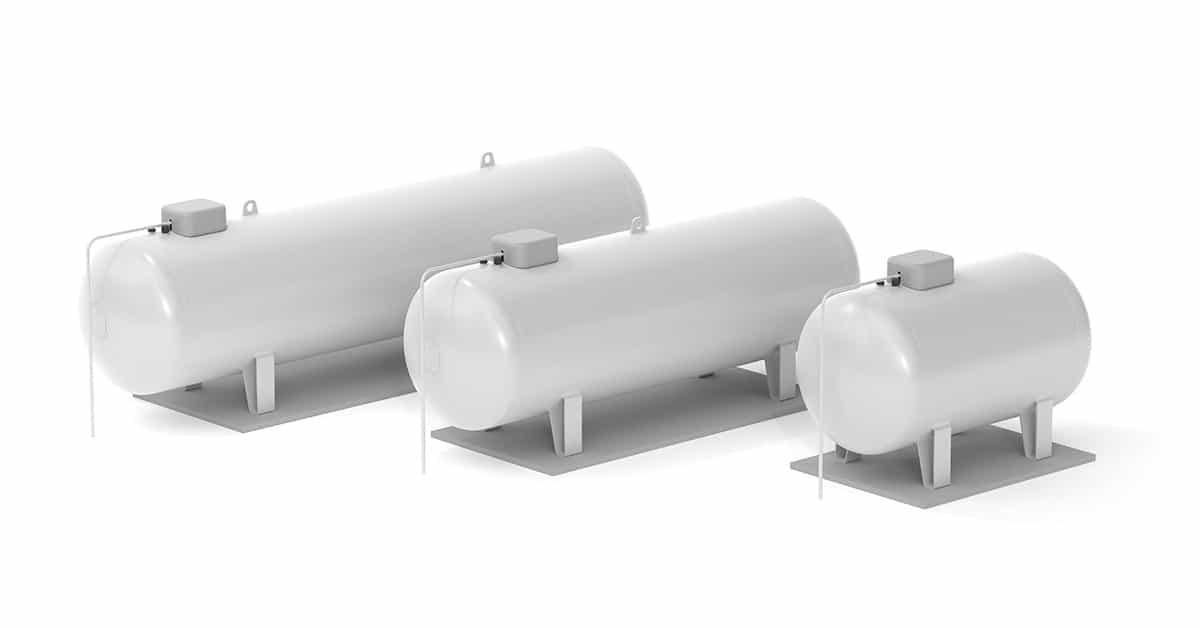
Typical Propane Tank Sizes
Propane tanks are typically measured in gallons, which refer to the tank’s water capacity. Some are measured in pounds. However, it’s important to note that propane is stored as a liquid under pressure, and a tank is usually filled to 80% of its total capacity to allow for gas expansion.
Common Propane Tank Sizes and Their Uses
Choosing the correct tank size ensures you have enough propane to meet your needs without frequent refilling while accommodating any potential increase in usage or additional appliances.
Here’s a list of different propane tank sizes and their uses.
Comparison chart:
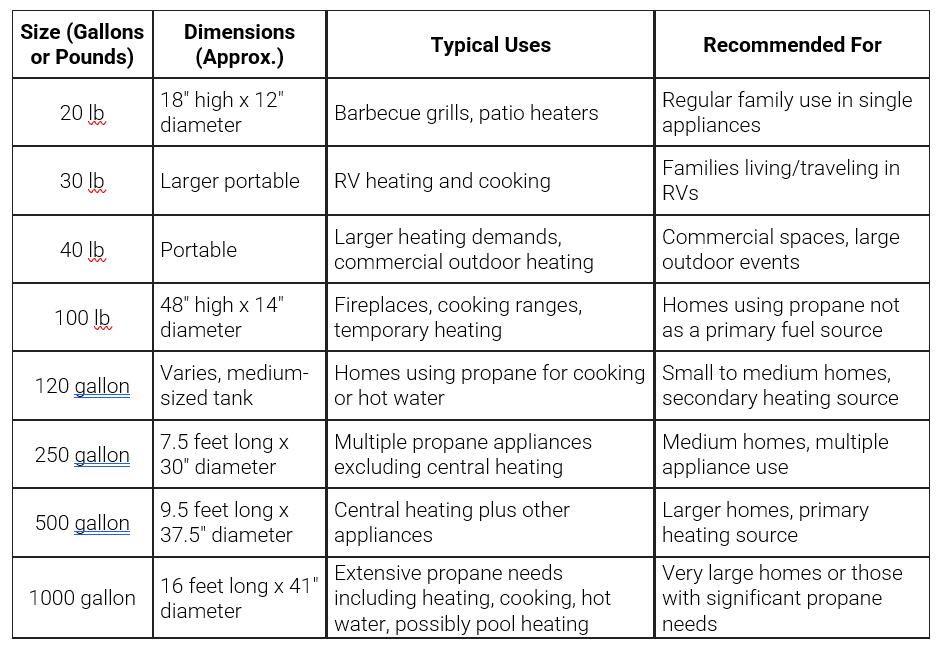
20 lb Propane Tank
- Capacity: Approximately 5 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 4 gallons.
- Dimensions: About 1 foot 6 inches tall and 12 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Most often used for gas grills, patio heaters, portable stoves, and small generators.
Placement: Always stored and used above ground, usually portable for easy transport.
100 lb Propane Tank
- Capacity: Approximately 23-25 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 23 gallons.
- Dimensions: Roughly 4 feet tall and 14 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Ideal for small appliances such as gas grills, space heaters, and backup generators.
Placement: Typically placed above ground.
100 Gallon Propane Tank
- Capacity: Holds 100 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 80 gallons.
- Dimensions: Approximately 4 feet 3 inches in length and 30 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Suitable for heating small homes, mobile homes, or fueling appliances like water heaters and stoves.
- Placement: Commonly installed above ground.
120 Gallon Propane Tank
- Capacity: Holds around 120 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 96 gallons.
- Dimensions: Roughly 54 inches tall and 30 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: A good choice for heating small homes or cabins, fueling multiple appliances such as furnaces, water heaters, clothes dryers, or fireplaces.
- Placement: Usually installed above ground, either vertically or horizontally, depending on the property layout.
250 Gallon Propane Tank
- Capacity: Holds about 250 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 200 gallons.
- Dimensions: Approximately 7 feet 10 inches in length and 30 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Appropriate for heating larger homes or powering multiple appliances such as water heaters, dryers, and fireplaces.
- Placement: Can be installed above ground or buried underground.
500 Gallon Propane Tank
- Capacity: Holds about 500 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 400 gallons.
- Dimensions: Approximately 9 feet 11 inches in length and 37.5 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Ideal for heating larger homes, fueling multiple appliances, or providing energy for commercial applications.
- Placement: Suitable for both above ground and underground installations.
1000 Gallon Propane Tank
- Capacity: Holds about 1000 gallons of propane. 80% usable capacity is 800 gallons.
- Dimensions: Approximately 16 feet 2 inches in length and 41 inches in diameter.
- Common Uses: Designed for large homes, agricultural operations, or commercial businesses with high propane demands.
Placement: Typically installed above ground or buried underground.
Estimating Your Propane Needs
Accurately estimating your propane needs is essential to choosing the right tank size and avoiding frequent refills or excess capacity. Here’s how to calculate your household’s propane consumption:
- List Appliances: Identify all propane-powered appliances in your home, including heaters, stoves, water heaters, and dryers.
- Determine Usage: Estimate how often each appliance is used. Consider how many hours per day it runs during the heating season. Estimate how many meals are cooked on the stove or oven each week.
- Calculate Consumption: Look up the BTU (British Thermal Unit) ratings for each appliance—this indicates the amount of propane they consume when in use. Convert these figures into gallons of propane based on the following conversion: One gallon of propane provides approximately 91,500 BTUs.
- Consider Seasonal Variations: Adjust your calculations based on seasonal changes. For example, heating needs will spike in winter, while water heating may remain constant throughout the year.
- Add a Buffer: To ensure you don’t run out of propane, add a 10-20% buffer to your estimated needs. This accounts for unexpected increases in usage.
By following these steps, you can develop a reasonably accurate estimate of your yearly propane consumption, aiding in the selection of an appropriately sized tank. Consulting with a propane supplier can provide professional insights and more precise assessments for those who need clarification on their calculations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Propane Tank Size
Selecting the right propane tank or cylinder involves several considerations that ensure efficiency, compliance, and safety. Here are key factors to evaluate:
- Home Size and Insulation: Larger homes or those with poor insulation may require larger tanks to meet home heating demands.
- Number of Propane Appliances: The more propane-powered appliances you have, the larger the tank you’ll need.
- Climate: Colder climates may necessitate larger tanks to ensure a sufficient fuel supply during winter months.
- Budget: Larger tanks have a higher initial cost but can be more economical over time due to less frequent refills.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a propane tank or cylinder that meets your current needs and accommodates future requirements and logistical constraints.
Installation and Safety Considerations
Proper installation and ongoing safety are paramount when using propane tanks and cylinders.
Note that for some homeowners, heating oil may be considered a safer alternative depending on the property layout and usage patterns. HOP Energy offers both propane and heating oil solutions, helping you choose the best and safest fuel option tailored to your home’s unique needs.
If you do go with propane, make sure you follow these key safety considerations and tips:
- Professional Installation: Always use qualified professionals to install propane tanks. They will ensure compliance with local codes and safety standards.
- Placement: Tanks should be placed on a non-flammable, solid foundation such as concrete and located away from the home’s main structure to reduce the risk of fire damage. Underground tanks require specific considerations for depth and protection against corrosion.
- Distance Regulations: Adhere to local regulations regarding the minimum distance between the tank and the house, property lines, and other structures. This helps in ensuring safety and ease of access for maintenance and refilling.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular inspections and maintenance with a certified technician. This includes checking for leaks, rust, and other potential safety hazards.
- Emergency Procedures: Ensure all household members know what to do in case of a propane leak, including how to turn off the propane supply and evacuate safely. Install propane detectors in the home to provide early warnings of leaks.
- Proper Usage: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for connecting and disconnecting appliances and cylinders. Never use outdoor propane appliances indoors.
By adhering to these installation and safety considerations, you can maintain a safe and efficient propane system in your home, minimizing risks while enjoying the benefits of propane energy.
The National Propane Gas Association is another good source of propane safety information.
Final Considerations
Selecting the right propane tank size is essential for efficient energy use and safety in your home. By considering factors such as home size, number of appliances, and climate, you can choose a tank that meets your home propane needs. Consulting with a propane professional like HOP can provide personalized recommendations to ensure optimal performance.
If you need further assistance or have specific questions about propane, propane tank, or home heating in general, feel free to reach out to us!

Frequently Asked Questions About Propane Tank Sizes
What are the most common propane tank sizes for homes?
Common residential propane tanks range from the 100 lb propane tank (about 24 gallons) for small appliances to larger tanks like the 250, 500, and 1000 gallon propane tanks used for whole-house heating and multiple appliances.
What size propane tank do I need for my house?
It depends on your total propane usage, including heating, cooking, and water heating. Most homes use tanks from 120 gallons up to 500 gallons, depending on house size and the number of propane appliances.
What is the difference between a 100 gallon propane tank and a 100 lb propane tank?
A 100 lb propane tank holds about 23.6 gallons of propane (by weight), while a 100 gallon tank holds 100 gallons of liquid propane. The 100 lb tank is much smaller and typically used for grills or small appliances.
How much propane do I need for a 2000-square-foot house?
For a 2000 sq. ft. home primarily heated with propane, a 500-gallon tank is usually recommended. Annual usage varies based on climate and insulation but typically falls between 1,200 and 1,500 gallons.
Can I install a large propane tank underground?
Yes, many large tanks, such as 250, 500, and 1000 gallon sizes, can be installed underground or above ground, depending on local codes and space.
Can a propane tank be installed right next to the house?
No, safety codes require propane tanks (100 gallons or larger) to be installed at least 10 feet away from the house or any ignition sources.
How far should a propane tank be from windows or openings?
Propane tanks should be placed at least 10 feet from any doors, windows, or vents to prevent fumes from entering the home.
What size propane tank do I need for a whole-house generator?
A 500-gallon propane tank is a common choice for whole-house generators, providing enough fuel for extended power outages, though tank size depends on your generator’s fuel consumption.
Are larger propane tanks more cost-effective?
Generally, yes. Larger tanks require less frequent refills, lowering delivery fees and ensuring a steady fuel supply, which can save money over time.
What is the largest propane tank used for residential purposes?
The largest common residential tank is 1000 gallons, suitable for large homes or properties with high propane needs, like farms or homes with multiple propane appliances.
How do I estimate my propane needs accurately?
Calculate your propane consumption by listing all propane appliances, estimating their usage, checking their BTU ratings, converting BTUs to gallons, and adding a 10-20% buffer for safety.
What safety considerations should I keep in mind when installing propane tanks?
Ensure professional installation, proper placement on a solid foundation, adherence to distance regulations, regular maintenance, and that everyone in your home knows emergency procedures.






